Imagine stepping into a world where digital elements blend seamlessly with our reality, or where you’re transported into a completely virtual universe. This isn’t science fiction – this is the power of immersive technology. It’s revolutionizing how we experience everything from entertainment to education and even work. In this guide, we’ll break down the core components of immersive technology: AR, VR, MR, and XR. Let’s dive in!
What is Immersive Technology?
At its core, immersive technology aims to pull users into a digital experience, either by enhancing their current environment or creating an entirely new one. It does this by interacting with our senses, especially sight and sound, to make digital content feel like a natural part of our surroundings.
But here’s where it gets interesting: immersive tech isn’t just one thing. It’s an umbrella term for a range of technologies that offer different levels of “immersion.” The most common forms are Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR). Together, they are often referred to as Extended Reality (XR).
Let’s break them down.
Augmented Reality (AR): Enhancing the Real World
Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital content—such as images, videos, or 3D models—onto the real world. You can still see your surroundings, but with added virtual elements that enhance your perception of reality.
How It Works:
AR works through devices like smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses that use cameras to detect the physical environment and place virtual objects on top of it. Apps like Snapchat filters or Pokémon Go are great examples of AR, where virtual characters and effects appear in real-world scenes through your device’s screen.
Applications:
- Retail: AR apps like IKEA Place allow users to visualize furniture in their own homes before purchasing.
- Education: AR can bring lessons to life, like interactive 3D models in textbooks.
- Healthcare: Surgeons use AR to overlay vital information during surgeries, improving precision and decision-making.
Virtual Reality (VR): Stepping into a New World
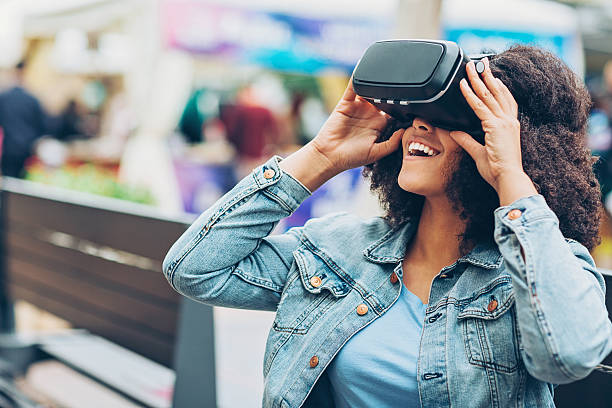

Virtual Reality (VR) is an immersive experience where users are placed in a fully digital environment that blocks out the real world. VR completely transports you to a new space, whether it’s a fantasy land, a training simulation, or a virtual meeting room.
How It Works:
Using VR headsets like Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, or PlayStation VR, users are visually and sometimes physically immersed in a 3D virtual environment. These headsets track head movements to ensure that you can look around and interact with the virtual space as if you were actually there.
Applications:
- Gaming: VR games let players explore and interact with virtual worlds in ways never possible before.
- Training: VR simulations are used for flight training, medical procedures, and even military exercises, offering risk-free, hands-on learning.
- Real Estate: Virtual property tours give buyers the chance to explore homes without visiting in person.
Mixed Reality (MR): The Best of Both Worlds
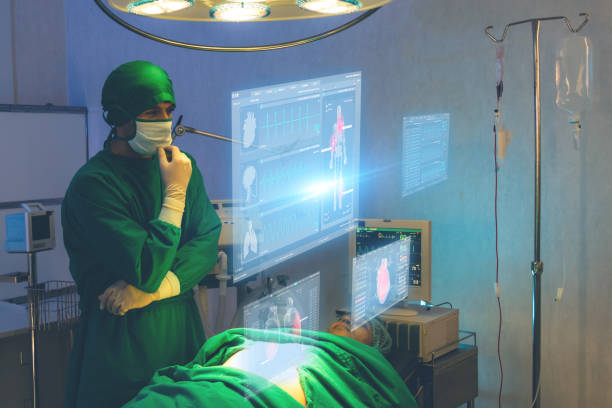
Mixed Reality (MR) is a hybrid technology that blends the real and virtual worlds, allowing digital objects to interact with the physical environment in real-time. Unlike AR, where virtual objects are simply placed in the real world, MR allows for dynamic interaction between both worlds.
How It Works:
Devices like Microsoft’s HoloLens use sensors and advanced cameras to map the physical world and allow users to interact with virtual objects as if they are part of the real world. For example, you can place a virtual 3D model of a machine on your desk and manipulate it using hand gestures.
Applications:
- Manufacturing: Engineers use MR to visualize and interact with machinery in real-time, helping with design and maintenance.
- Healthcare: MR is used for complex surgeries where doctors need to interact with both digital guides and real patients.
- Entertainment: MR can bring interactive, holographic characters into your living room for unique entertainment experiences.
Extended Reality (XR)
Extended Reality (XR) is an umbrella term that covers all immersive technologies, including AR, VR, and MR. XR represents the entire spectrum of real and virtual environments and includes any technology that enhances or creates immersive experiences.
How It Works:
XR is not one single technology but rather the combination of AR, VR, and MR. With XR, users can seamlessly switch between different levels of immersion, from virtual environments to real-world overlays, depending on the device they use and the experience they want to create.
Applications:
- Education: XR offers a range of learning experiences, from VR classrooms to AR-enhanced textbooks.
- Retail: XR shopping experiences allow customers to try products virtually or explore virtual showrooms.
- Training and Development: XR is widely used for immersive training experiences across industries, offering the flexibility of VR and AR combined.
Conclusion: The Future of Immersive Technology
Immersive technology is revolutionizing how we learn, work, shop, and play. Whether it’s AR enhancing our real world, VR transporting us to a different realm, or MR merging both worlds, these technologies are making experiences more interactive and engaging. As XR continues to evolve, it will unlock even more possibilities for businesses, educators, and creators to provide immersive experiences.
Immersive technology is not just a glimpse into the future—it’s already here, shaping the world around us in incredible ways. Stay tuned for exciting developments as these technologies continue to transform industries and daily life.

