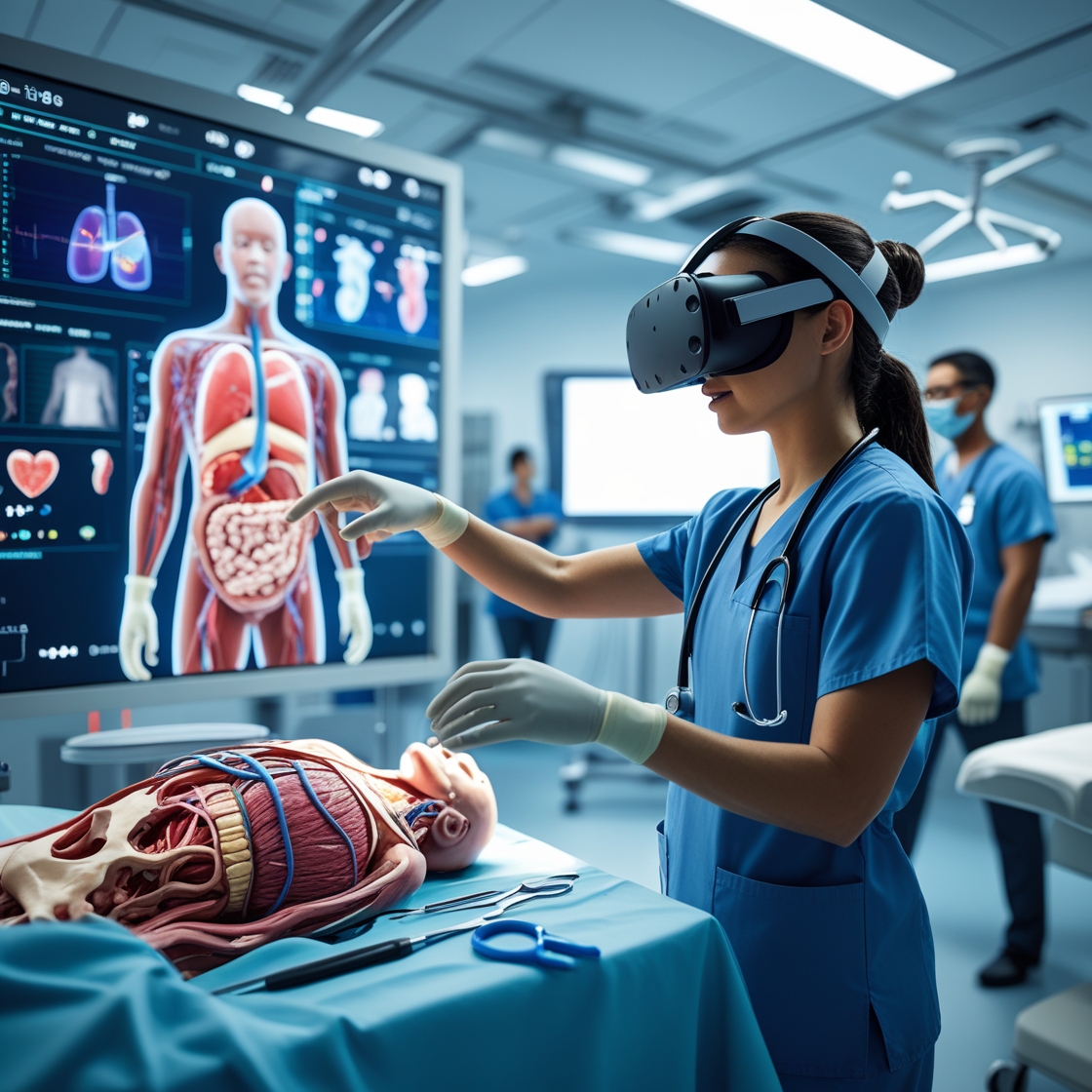
Medical training has always required precision, patience, and practice. But how do you prepare for life-and-death decisions in a classroom setting? Enter Virtual Reality (VR) — a revolutionary technology transforming how future healthcare professionals learn, train, and succeed.
By immersing students in realistic clinical environments, VR is bridging the gap between textbook knowledge and real-world application — safely, efficiently, and at scale.
What is Virtual Reality in Healthcare Training?
Virtual Reality is an interactive 3D environment that mimics real-life settings. With the help of headsets, motion sensors, and controllers, learners can step into a virtual world — like an operating room, emergency ward, or anatomy lab — and interact just as they would in real life.
In healthcare, VR is used to simulate surgeries, patient interactions, emergency scenarios, and medical procedures. The goal? To give students and professionals a safe, controlled space to practice, fail, learn, and repeat — without risking patient lives.
How Does Virtual Reality Work in Medical Training?
Here’s how it works step-by-step:
- Hardware: Learners wear VR headsets like Meta Quest or HTC Vive that block out the real world and display a 360-degree digital environment.
- Sensors and Controllers: These detect motion, hand gestures, or eye movements, allowing users to interact with virtual tools, patients, and objects.
- Simulation Software: Medical VR platforms like Osso VR, Touch Surgery, or SimX simulate real-world procedures, complete with accurate anatomy and scenarios.
- Feedback and Analytics: Systems track learner performance and provide feedback, helping users correct mistakes, measure efficiency, and improve over time.
It’s like flight simulation for surgeons, nurses, and paramedics — only far more detailed and interactive.
Real-World Applications of VR in Healthcare Training
🔪 1. Surgical Simulation
VR enables aspiring surgeons to rehearse operations — from laparoscopic procedures to brain surgeries. They can visualize anatomy in 3D, perform each step virtually, and repeat until confident, without needing a live patient.
🚨 2. Emergency Response and Trauma Training
VR prepares medical professionals for high-stakes situations like heart attacks, strokes, or trauma cases. These time-critical simulations improve reaction times and decision-making skills under pressure.
👩⚕️ 3. Nursing and Patient Care Training
Nurses use VR to learn IV insertions, monitor vitals, manage post-operative care, and even practice patient communication. It builds both clinical skills and emotional intelligence.
🧠 4. Mental Health Therapy Education
Trainees experience simulated scenarios involving PTSD, anxiety, or schizophrenia to understand what patients endure. This builds empathy and improves diagnosis and counseling skills.
🗣️ 5. Soft Skills and Communication
Not all training is technical. VR helps learners navigate difficult conversations — like delivering bad news or handling sensitive patient issues — by placing them in realistic social simulations.
👶 6. Pediatric and Geriatric Training
VR allows users to understand age-specific care — like managing a child with fever or understanding an elderly patient’s mobility limitations.
Global Impact: VR Makes Medical Training More Accessible
One of the biggest strengths of VR is its scalability. Whether you’re in a top university hospital or a rural clinic, VR allows access to the same world-class training modules. No more dependency on cadavers, limited faculty time, or expensive lab equipment.
It’s portable, affordable, and democratizing medical education across the globe.
Benefits of VR in Healthcare Training
Here’s why VR is gaining ground so quickly:
- 🧪 Risk-Free Learning: Practice without consequences. Mistakes become valuable lessons.
- 🔁 Repetition Leads to Mastery: Procedures can be practiced as many times as needed.
- 📊 Performance Tracking: Get detailed analytics and personalized feedback.
- ⏱️ Time and Cost Efficient: Reduces the need for physical setups and instructors.
- 🌐 Remote Learning Capable: Learn anytime, anywhere, making training accessible during crises like COVID-19.
- ❤️ Builds Confidence: Learners feel more prepared before touching a real patient.
- 🎮 Gamified Engagement: The interactive format keeps learners motivated and engaged.
The Future of VR in Medical Education
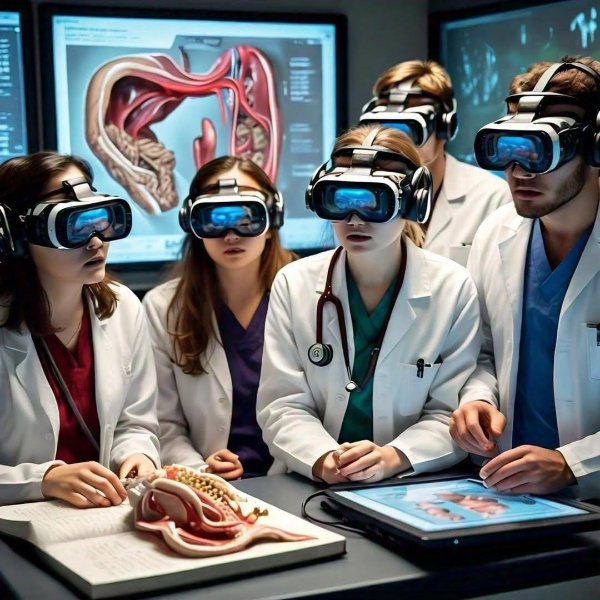
The horizon for Virtual Reality in medical education is incredibly exciting. As technology evolves, so does the potential for even more immersive, intelligent, and collaborative training experiences. One of the most promising developments is AI-driven adaptive learning, where virtual tutors can tailor scenarios and feedback based on a learner’s individual performance, creating a personalized growth path.
Another breakthrough on the rise is haptic feedback — gloves and tools that simulate the sensation of touch, allowing users to feel the resistance of tissue or the rhythm of a pulse, bringing an unmatched level of realism to virtual procedures. We’re also seeing the rise of multi-user VR environments, where entire healthcare teams can train together in synchronized simulations, improving collaboration and communication.
Mixed Reality (MR) is set to play a huge role too, seamlessly blending real-world settings with virtual overlays for hybrid learning experiences. And with cloud-based VR libraries, institutions can share, update, and access training modules anytime, anywhere, making learning both flexible and future-ready.
By 2030, it’s anticipated that Virtual Reality will become a standard fixture in the training programs of every leading medical institution — not as a supplement, but as a core component of education.
Why Choose VR for Healthcare Training?
With so many changes sweeping across the medical field, many wonder if investing in Virtual Reality is truly worthwhile. The answer lies in the growing demands of modern healthcare education. Traditional training methods often struggle with scalability and offer limited room for error — a risky combination in a profession where lives are at stake. Meanwhile, today’s students expect more interactive and technology-driven learning experiences that mirror the real world.
Educational institutions are also seeking solutions that are cost-effective, consistent, and capable of being repeated without added strain on resources. Most importantly, patients deserve to be treated by professionals who are not only knowledgeable but also confident and well-practiced. VR checks all these boxes. It enables immersive, flexible, and safe training that equips future caregivers to perform at their best — making it not just an option, but an essential evolution in medical education.
Conclusion: VR is Not Just the Future — It’s the Present
Virtual Reality is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a practical, powerful tool already reshaping how we train healthcare professionals. From performing surgery to offering compassionate care, VR ensures learners are better prepared, more confident, and ultimately, more effective.
As we look ahead, integrating VR into medical education is not just a tech upgrade — it’s a lifesaving evolution.